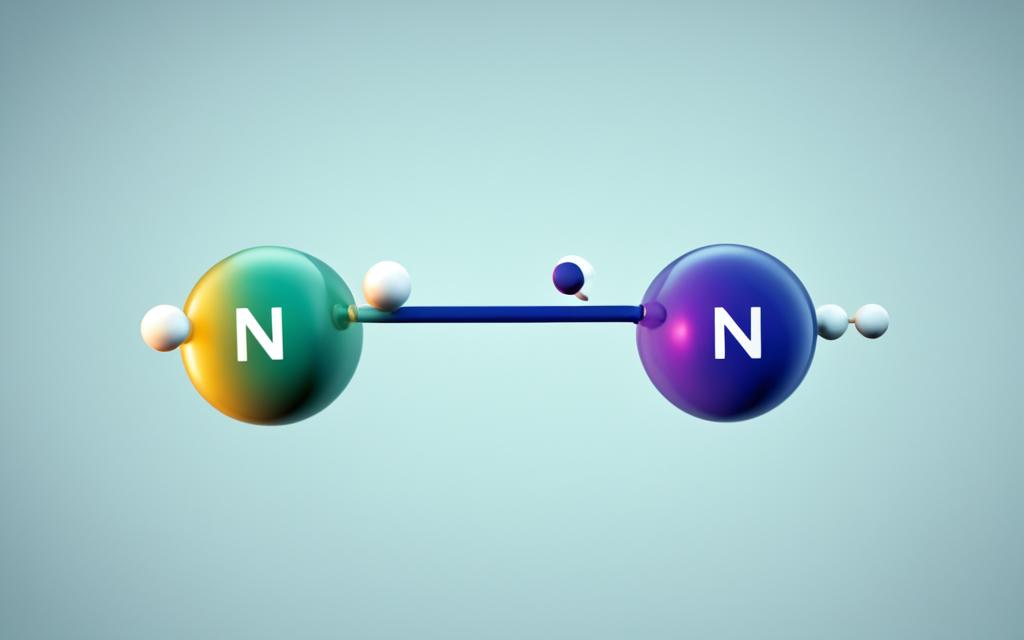
The molar mass of N2, or nitrogen gas, is a fundamental concept in chemistry that represents the mass of one mole of the nitrogen molecule. Understanding the molar mass of N2 is crucial for various chemical calculations, reactions, and processes. In this article, we will explore the definition of molar mass, how to calculate the molar mass of N2, and the importance of this value in chemistry.
Understanding the Concept of Molar Mass
Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, where a mole is defined as the amount of a substance that contains the same number of particles (atoms, molecules, or ions) as there are atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12. The molar mass is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol) and is a fundamental property of a chemical substance. Knowing the molar mass of a substance is essential for understanding chemical reactions, stoichiometry, and the behavior of materials in various applications.
To calculate the molar mass of a substance, you need to know the atomic masses of the elements that make up the substance and the number of atoms of each element in the molecular formula. By multiplying the atomic mass of each element by the number of atoms of that element in the molecule, and then adding up the masses of all the elements, you can determine the molar mass of the substance.
The importance of molar mass lies in its fundamental role in various areas of chemistry. It is essential for understanding the relationships between the quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions, known as stoichiometry. Molar mass also plays a crucial role in the study of the physical properties of materials, such as their density, concentration, and behavior in various processes and applications.
By mastering the concept of molar mass, you can unlock a deeper understanding of the chemical world and enhance your ability to solve problems, design experiments, and optimize processes in a wide range of fields, from biochemistry to materials science.
Molar Mass of N2
The molar mass of N2, or nitrogen gas, is the mass of one mole of nitrogen molecules. To calculate the molar mass of N2, you need to know the atomic mass of the nitrogen element and the number of atoms in the nitrogen molecule. The atomic mass of nitrogen is 14.01 g/mol, and since the nitrogen molecule (N2) consists of two nitrogen atoms, the molar mass of N2 is 28.02 g/mol. This value is crucial for understanding the behavior of nitrogen gas in various chemical reactions and processes.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Atomic Mass of Nitrogen | 14.01 g/mol |
| Number of Nitrogen Atoms in N2 | 2 |
| Molar Mass of N2 | 28.02 g/mol |
The molar mass of N2 is an essential parameter in understanding the properties and behavior of nitrogen gas in various chemical applications. By mastering the concept of molar mass and the specific molar mass of N2, you can enhance your understanding of chemistry and apply this knowledge to a wide range of scientific and industrial processes.
Applications of Nitrogen’s Molar Mass
The molar mass of N2, or nitrogen gas, has numerous applications in chemistry and related fields. It is used in stoichiometric calculations to determine the quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions involving nitrogen. Additionally, the molar mass of N2 is essential for calculating the density of nitrogen gas, which is important in gas storage, transportation, and industrial applications.
Furthermore, the molar mass of N2 is a crucial parameter in the design and optimization of various processes, such as the production of ammonia, the fixation of nitrogen, and the study of atmospheric chemistry. Understanding the importance of nitrogen molar mass is crucial for these applications, as it allows for accurate measurements, predictions, and adjustments in various chemical and industrial processes.
The uses of nitrogen molar mass extend beyond just chemical calculations and processes. It also plays a vital role in the understanding and management of gas storage and transportation, ensuring the efficient and safe handling of nitrogen gas in various industries. By mastering the concept of nitrogen’s molar mass, you can leverage this knowledge to optimize your applications and enhance your overall understanding of chemistry.
Factors Affecting the Molar Mass of N2
The molar mass of N2, or nitrogen gas, can be influenced by various factors affecting molar mass of n2, such as temperature and pressure. As the temperature increases, the average kinetic energy of the nitrogen molecules also increases, leading to a slight decrease in the molar mass. Conversely, an increase in pressure can cause a slight increase in the molar mass of N2 due to the compression of the gas. However, these changes are typically small and have a negligible impact on most chemical calculations and processes involving nitrogen gas.
| Factor | Effect on N2 Molar Mass |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Increase in temperature leads to a slight decrease in molar mass |
| Pressure | Increase in pressure leads to a slight increase in molar mass |
It’s important to note that these variables influencing n2 molar mass are typically small and have a negligible impact on most chemical calculations and processes involving nitrogen gas. Understanding the conditions that change n2 molar mass can help you make more accurate calculations and better understand the behavior of nitrogen in various applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the molar mass of N2, or nitrogen gas, is a fundamental property that is essential for understanding and calculating various chemical processes and reactions. By learning how to calculate the molar mass of N2 and understanding its importance, you can better navigate the world of chemistry and apply this knowledge to a wide range of applications, from stoichiometric calculations to gas storage and industrial processes.
The key takeaways on nitrogen molar mass are that it represents the mass of one mole of nitrogen molecules, and this value is crucial for numerous chemical calculations and applications. Understanding the summary of N2 molar mass and its implications will provide you with a valuable tool in your chemistry toolkit, allowing you to tackle a variety of problems and optimize various processes involving nitrogen gas.
Mastering the concept of molar mass, and specifically the molar mass of N2, will empower you to make informed decisions, enhance your problem-solving skills, and deepen your understanding of the fundamental principles of chemistry. As you continue to explore the conclusion on molar mass of N2, you’ll find that this knowledge serves as a foundation for further learning and practical applications in your scientific endeavors.