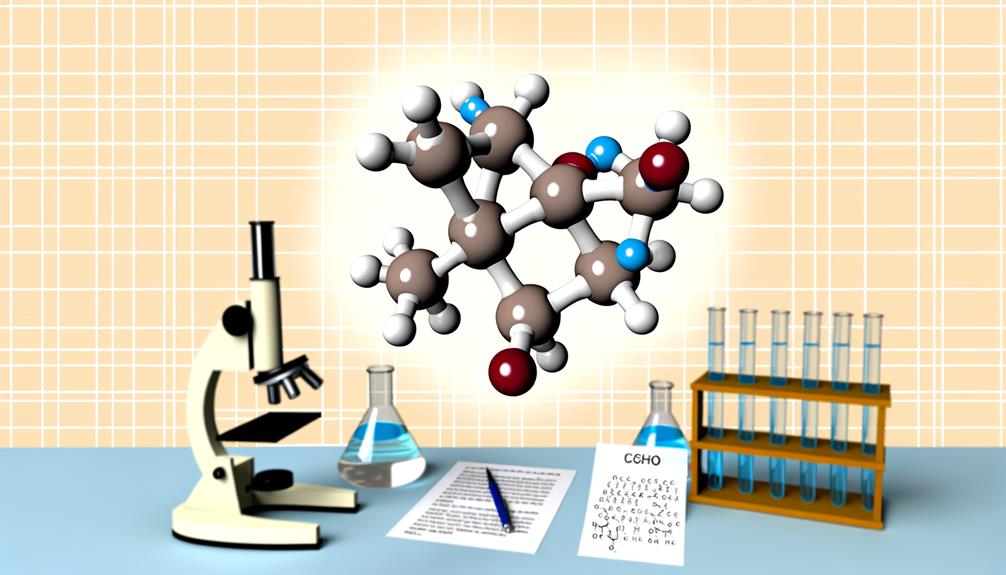
Did you know that C6H12O6, also known as glucose, is the primary source of energy for the human body? It’s fascinating how this simple molecule powers every cell in your body, from your brain to your muscles. You’ll be intrigued to explore its structure, function, and significant roles in our health and wellbeing.
Isn’t it exciting to find out how this little compound is so essential to life as we know it?
Let’s uncover more about this biochemical marvel.
The basic structure of C6H12O6
Diving right into the core, C6H12O6, often known as glucose, is a complex molecule with a unique and intriguing structure that you’ll find fascinating. It’s composed of six carbon (C) atoms, twelve hydrogen (H) atoms, and six oxygen (O) atoms. If you picture it, imagine a ring-like structure, where five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom form the ring, and the sixth carbon atom juts out from one of the carbon atoms in the ring.
Interestingly, the hydrogen and oxygen atoms aren’t just hanging around aimlessly. They’re attached to the carbon atoms, creating a compact, well-organized structure. You’ll also find that there’s a balance between the atoms – for every carbon atom, there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, which gives us the chemical formula C6H12O6.
Furthermore, glucose can exist in two forms, alpha and beta, which differ in the orientation of the hydroxyl group at the anomeric carbon. It’s like having a left-handed and a right-handed version of the molecule!
In essence, the structure of C6H12O6 isn’t just random. It’s a well-thought-out masterpiece of nature, showing us the beauty of molecular design.
Role of C6H12O6 in human body
In your body, C6H12O6 plays a pivotal role as the primary source of energy, fueling every cell to perform its functions effectively. You may know it better as glucose, a simple sugar that’s vital for your survival. It’s not just about energy, though. This molecule is instrumental in various biological processes that keep you running smoothly.
For instance, it’s involved in the synthesis of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. So, when you’re building muscle or repairing tissues, you’re relying on glucose. It also plays a part in the production of nucleic acids, the components of your DNA and RNA. That’s crucial for cell division and genetic information transmission.
Moreover, your brain primarily depends on glucose for its functions. Your neurons can’t store glucose, so they rely on the constant supply from the blood stream. Without glucose, your thinking, learning, and memory would be impaired.
In essence, C6H12O6 is like the fuel for your body’s engine, powering everything from your muscles to your mind. Maintaining a steady level of glucose in your blood is key to your overall health and well-being. That’s why it’s important to understand the role of C6H12O6 in your body.
C6H12O6 in energy production
When it comes to energy production, you can’t ignore the significant role that C6H12O6, or glucose, plays in your body. It’s your body’s preferred source of energy, acting as the fuel that powers all your bodily functions.
Once you’ve consumed food, your body gets to work breaking it down into simple sugars, primarily glucose. This glucose then enters your bloodstream, ready to be transported to where it’s needed most. Your brain, muscles, and other organs eagerly await this energy delivery.
The magic really happens in your cells, where glucose is converted into adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through a process called cellular respiration. ATP is like the currency of energy in your body, and your cells spend it to power all their activities.
But what if you’ve eaten more glucose than your body needs right now? Don’t worry, your body’s got a plan for that too. It cleverly converts the extra glucose into glycogen, a form of storage that can be quickly turned back into glucose when needed.
The impact of C6H12O6 on health
While it’s crucial for energy, too much glucose, or C6H12O6, in your body can lead to health issues. Your body needs to maintain a delicate balance. If you take in more glucose than your body can use, it doesn’t just get stored for later. Instead, it can lead to weight gain, and ultimately, obesity.
But that’s not all. Excess glucose can also have an impact on your body’s insulin production. In a healthy body, insulin helps to regulate glucose levels. But when there’s too much glucose, your body might stop responding to insulin as well as it should. This could lead to type 2 diabetes, a condition that can have serious long-term impacts on your health.
And let’s not forget about your heart. High glucose levels can increase your risk of heart disease, one of the leading causes of death worldwide. So, while C6H12O6 is essential for your body to function properly, it’s a classic case of ‘too much of a good thing’. Understanding the impact of C6H12O6 on health is vital to maintaining a balanced lifestyle and avoiding potential health complications.
Other significant functions of C6H12O6
Beyond its impact on health, glucose plays several other key roles in your body that you mightn’t be aware of. It’s the primary fuel source for your brain, which consumes about 120 grams of glucose daily. That’s nearly two-thirds of the total amount of glucose used by your body. Without it, your brain wouldn’t function properly.
Glucose also plays a significant role in cell growth and reproduction. It’s involved in the synthesis of nucleic acids, the building blocks of your DNA. Moreover, glucose acts as a precursor for several amino acids, which are essential for protein synthesis.
Did you know that glucose is also crucial for your body’s immune system? It provides energy to white blood cells, enabling them to fight off infections and diseases.
Conclusion
So, you’ve now cracked the code of C6H12O6!
It’s not just a complex formula, but a vital component of your body, playing a key role in energy production and impacting your health in significant ways.
Remember, understanding such molecules helps you appreciate the intricate workings of your body.
Keep exploring, keep learning, and you’ll unravel more fascinating truths about the world within you!