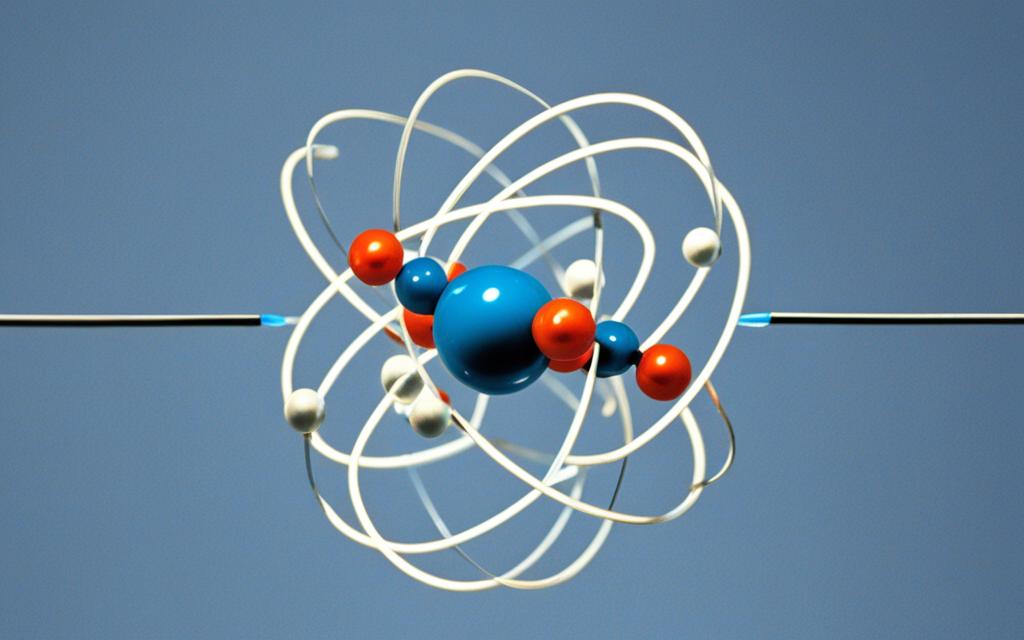
The Helium Bohr Model provides a comprehensive understanding of the atomic structure of the helium element. This model, developed by renowned physicist Niels Bohr, offers valuable insights into the behavior and characteristics of helium atoms. By exploring the Helium Bohr Model, you’ll uncover the fundamental principles that govern the arrangement and behavior of electrons within a helium atom, as well as the implications of this model for our broader understanding of atomic theory.
Understanding the Bohr Model
The Bohr Model, proposed by renowned physicist Niels Bohr in 1913, is a foundational theory that describes the structure of atoms. This model postulates that electrons in an atom occupy discrete energy levels, or “shells,” around the nucleus. Each energy level has a specific amount of energy associated with it, and electrons can only exist in these defined energy levels. This concept of quantized energy levels is a key aspect of the Bohr Model and lays the groundwork for understanding the behavior of atoms, including the helium atom.
The Bohr Model revolutionized our understanding of atomic structure by introducing the idea that electrons are not randomly distributed around the nucleus, but rather organized into specific energy levels. This model explains how electrons can only transition between these discrete energy levels, absorbing or emitting energy in the form of photons as they do so. This fundamental principle laid the foundation for the development of more advanced theories, such as quantum mechanics, which provide a more comprehensive and accurate description of atomic structure and behavior.
By understanding the Bohr Model and its principles, you can gain valuable insights into the electron configuration of atoms, including the arrangement and behavior of electrons within the helium atom. This knowledge is essential for comprehending the properties and characteristics of various elements, as well as for advancing our understanding of the microscopic world.
Helium Bohr Model
The Helium Bohr Model is a specific application of the Bohr Model to the helium atom. Helium, a noble gas, has a unique atomic structure characterized by two protons in the nucleus and two electrons orbiting the nucleus. According to the Helium Bohr Model, the two electrons in a helium atom occupy the innermost energy level, known as the 1s shell. This configuration is the most stable and energy-efficient arrangement for the helium atom, as the electrons are tightly bound to the nucleus and do not participate in chemical reactions.
The electron configuration of helium, as described by the Bohr Model, is a key feature of the Helium Bohr Model. The two electrons in a helium atom fill the 1s orbital, which is the lowest energy level available. This closed-shell configuration results in a highly stable and non-reactive atom, as the electrons are not available for participation in chemical processes.
The stability and inert nature of the helium atom, as illustrated by the Helium Bohr Model, have important implications for our understanding of atomic structure and behavior. This model provides a foundation for the development of more advanced theories, such as quantum mechanics, which offer a more comprehensive and accurate description of the atomic structure of helium and other elements.
Visualizing the Helium Atom
The Helium Bohr Model can be visually represented in the form of a diagram, which helps to illustrate the arrangement and behavior of the electrons within the helium atom. In this diagram, the nucleus of the helium atom, containing two protons, is depicted at the center. Surrounding the nucleus are the two electrons, orbiting in the innermost 1s energy level.
This visual representation provides a clear and intuitive understanding of the spatial arrangement and electron configuration of the helium atom, as described by the Bohr Model. By visualizing the helium atom in this way, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the fundamental principles that govern the behavior of this unique element.
Key Features and Characteristics
The Helium Bohr Model highlights several key features and characteristics of the helium atom. Firstly, the two electrons in a helium atom are tightly bound to the nucleus, occupying the innermost 1s energy level. This configuration results in a highly stable and non-reactive atom, as the electrons are not available for participation in chemical reactions. Additionally, the Helium Bohr Model explains the closed-shell electronic structure of helium, which contributes to its inert nature and the fact that it is a noble gas.
Understanding these fundamental characteristics of the helium atom, as described by the Bohr Model, is essential for comprehending the behavior and properties of this element. The stability of the helium atom is a direct result of the key features of the Helium Bohr Model, which provide valuable insights into the atomic structure and behavior of this unique noble gas.
| Key Features of Helium Bohr Model | Characteristics of Helium Atom | Stability of Helium Atom |
|---|---|---|
| – Electrons occupy the innermost 1s energy level – Closed-shell electronic configuration |
– Highly stable and non-reactive – Inert noble gas |
– Tightly bound electrons – No available electrons for chemical reactions |
By understanding the key features and characteristics of the helium atom as outlined in the Helium Bohr Model, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the stability and unique properties of this element, which are fundamental to its role in the periodic table and its various applications.
Implications for Atomic Theory
While the Helium Bohr Model may not be a complete or entirely accurate representation of atomic structure, it has made significant contributions to our understanding of atomic theory. This model laid the groundwork for the development of more advanced theories, such as quantum mechanics, which provide a more comprehensive and accurate description of atomic structure and behavior.
The Helium Bohr Model’s emphasis on quantized energy levels and the stability of the helium atom’s electron configuration paved the way for the development of quantum mechanical principles. These principles have vastly expanded our knowledge of the fundamental nature of atoms and the behavior of subatomic particles. By understanding the Helium Bohr Model and its limitations, you can better appreciate the evolution of atomic theory and the ongoing advancements in our understanding of the microscopic world.
The implications of the Helium Bohr Model are far-reaching, as it has laid the foundation for the development of more sophisticated theories that continue to shape our understanding of the atomic world. As you explore the Helium Bohr Model, you’ll gain valuable insights into the contributions to atomic theory and the importance of this model in the broader context of the scientific journey to unravel the mysteries of the universe.